Q-Switched Laser
Q-Switched Laser
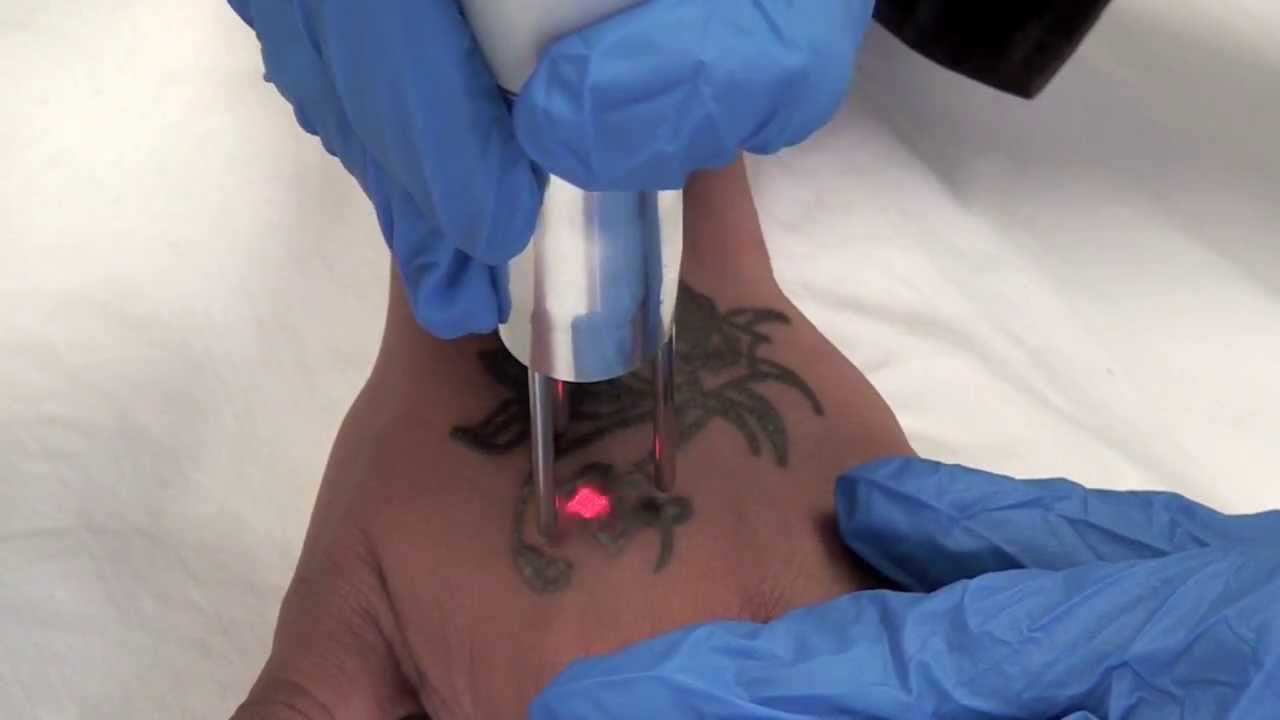
Q-switched lasers are a specific type of laser technology used in dermatology and cosmetic procedures. They are known for delivering high-intensity laser pulses in very short durations, making them highly effective for certain skin treatments. Q-switched lasers offer an effective solution for various cosmetic and dermatological issues, providing precision and efficacy with minimal downtime
How Q-Switched Lasers Work
- Laser Pulse: Q-switched lasers emit a single, high-energy pulse that lasts only a few nanoseconds.
- Mechanism: The laser energy is absorbed by specific pigments (such as melanin in the skin or ink in tattoos), causing them to break down into smaller particles. The body’s natural processes then remove these particles over time.
Applications
Tattoo Removal
- Effectiveness: Q-switched lasers are particularly effective for removing tattoos of various colors. The laser targets the ink pigment without significantly affecting the surrounding skin.
- Sessions: Multiple sessions are usually required to achieve desired results, depending on the tattoo’s size, color, and depth.
Pigmented Lesions
- Types: These include age spots, sun freckles, Stubborn melasma, brown spots and other forms of hyperpigmentation.
- Procedure: The laser targets the excess melanin in the skin, breaking it down and allowing it to be naturally eliminated by the body.
- Q- switch laser can also safely treat many forms of birthmarks ranging from brown to blue-grey in color including Cafe-au-lait spots, Nevus of Ota and Hori’s nevus
- Lightening areas that are highly sensitive to other types of lasers and peeling
- Removing lip pigmentation, such as pigmentation resulting from smoking or some diseases that affect the lips
Skin Rejuvenation
- Benefits: Q-switched lasers can improve skin texture, reduce fine lines and wrinkles, and enhance overall skin tone by stimulating collagen production.
- Techniques: Procedures such as laser toning use Q-switched lasers for these effects.
Acne Scar Treatment
- Mechanism: The laser targets scar tissue, promoting the growth of new, healthy skin cells and collagen.
Considerations
- Multiple Sessions: Often needed to achieve optimal results, especially for tattoo removal or deep pigmentation issues.
- Side Effects: Temporary redness, swelling, and slight discomfort. Rarely, changes in skin color or texture may occur.
- Cost: Varies depending on the size of the treatment area, the number of sessions required, and the specific condition being treated.
Aftercare
- Sun Protection: Essential to avoid pigmentation changes and protect the treated area.
- Gentle Skincare: Use mild products and avoid harsh chemicals or treatments until the skin heals.
- Follow-Up: Adhering to the recommended treatment schedule and follow-up appointments for best results.
Q-switched and Melasma – Clinic challenges:
Q-switched lasers offer a promising option for managing melasma, especially when combined with other treatments and proper skincare routines. It is essential to consult with a dermatologist experienced in treating melasma to develop a tailored treatment plan that minimizes the risk of side effects and optimizes results. Melasma is a chronic skin condition characterized by dark, hyperpigmented patches, typically on the face. Melasma is often triggered or worsened by factors such as sun exposure, hormonal changes (like those during pregnancy or from birth control), and genetic predisposition.
How Q-switched Lasers Work on Melasma:
- Targeting Pigment: Q-switched lasers emit high-intensity light in very short pulses (nanoseconds). This light targets and breaks down the melanin (pigment) within the skin cells without damaging the surrounding tissue. The fragmented pigment particles are then naturally eliminated by the body’s immune system.
- Selective Photothermolysis: The laser’s energy is selectively absorbed by the pigmented areas, making it highly effective for treating hyperpigmentation while minimizing the risk of affecting the surrounding skin.
Benefits of Using Q-switched Lasers for Melasma:
- Effective on Epidermal and Dermal Melasma: Q-switched lasers can treat both superficial (epidermal) and deeper (dermal) melasma.
- Minimal Downtime: The procedure is usually well-tolerated with minimal recovery time, allowing patients to return to their daily activities quickly.
- Improvement in Skin Tone: In addition to reducing pigmentation, Q-switched lasers can improve overall skin tone and texture.
Types of Q-switched Lasers Commonly Used:
- Q-switched Nd Laser: This is one of the most commonly used lasers for melasma treatment. It can penetrate deeply into the skin, making it effective for dermal melasma. It typically operates at a wavelength of 1064 nm, which is ideal for treating darker skin types.
- Q-switched Ruby Laser: This laser operates at a wavelength of 694 nm and is effective for lighter skin types. However, it is less commonly used due to a higher risk of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, especially in darker skin tones.
- Q-switched Alexandrite Laser: Operating at a wavelength of 755 nm, it’s another option but is less frequently used for melasma due to similar concerns about pigmentation in darker skin types.
Considerations and Precautions:
- Risk of Recurrence: Melasma is a chronic condition, and while Q-switched lasers can significantly reduce pigmentation, the condition may recur, especially with ongoing sun exposure or hormonal changes.
- Multiple Sessions: Treatment usually requires multiple sessions spaced weeks apart to achieve the desired results.
- Combination Therapies: Often, Q-switched laser treatment is combined with other therapies such as topical depigmenting agents (e.g., hydroquinone, tretinoin), chemical peels, or sunscreen to enhance results and prevent recurrence.
- Post-treatment Care: Strict sun protection is crucial after laser treatment to prevent the worsening or recurrence of melasma. This includes using a high-SPF sunscreen and avoiding direct sun exposure.
Potential Side Effects:
- Temporary Redness and Swelling: Mild redness and swelling are common immediately after the treatment but usually resolve within a few hours to days.
- Post-inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH): Although less common with Q-switched lasers than with some other treatments, PIH can still occur, particularly in darker skin tones.
Advantages of using Q-switched laser over any other laser devices
- Excimer Lasers Work on Melasma as the excimer laser delivers a focused beam of UVB light directly to the hyperpigmented areas. This light helps to reduce excess melanin production, which can lead to the lightening of the dark patches associated with melasma.
- The excimer laser is a potential treatment option for melasma, especially in cases where other treatments have not been fully effective. However, it is not as commonly used for melasma as Q-switched lasers or fractional lasers so it can be particularly useful for cases of melasma that are resistant to other treatments, such as topical creams or chemical peels.
- Fractional Lasers: Fractional lasers, which treat a fraction of the skin at a time, are also commonly used for melasma and may be combined with other therapies. The excimer laser, in contrast, focuses on very specific areas and is typically used in a more localized manner.
Q-switched and Tattoos – Clinic challenges:
Factors on which the effectiveness of removing tattoos and various pigmentations depends:
- Color of the tattoo: There are rare colors of tattoos that may take a larger number of sessions to remove
- Skin color: The greater the difference between the skin color and the color of the tattoo, the better and faster the results will be
- Overlapping of colors, as this type of tattoo requires the use of more than one type of laser to remove it
- The history of making tattoos: the older it is, the easier it is to remove
- The size of the tattoo, the smaller the size, the easier it is to remove
- The place of tattooing is where foot tattoos require a lot of gel polish especially for tattoo removal or deep
- The density of the tattoo color, the higher the density, the more sessions it requires
